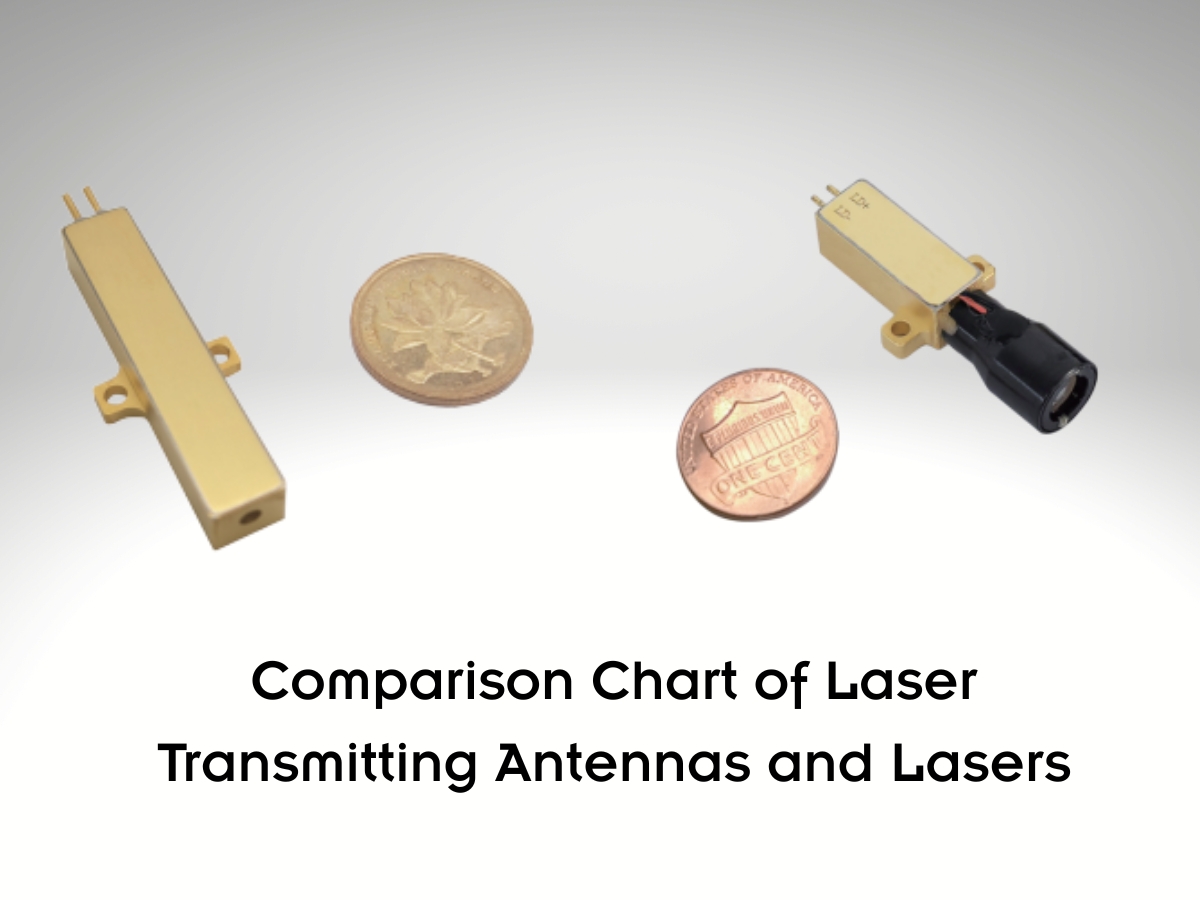
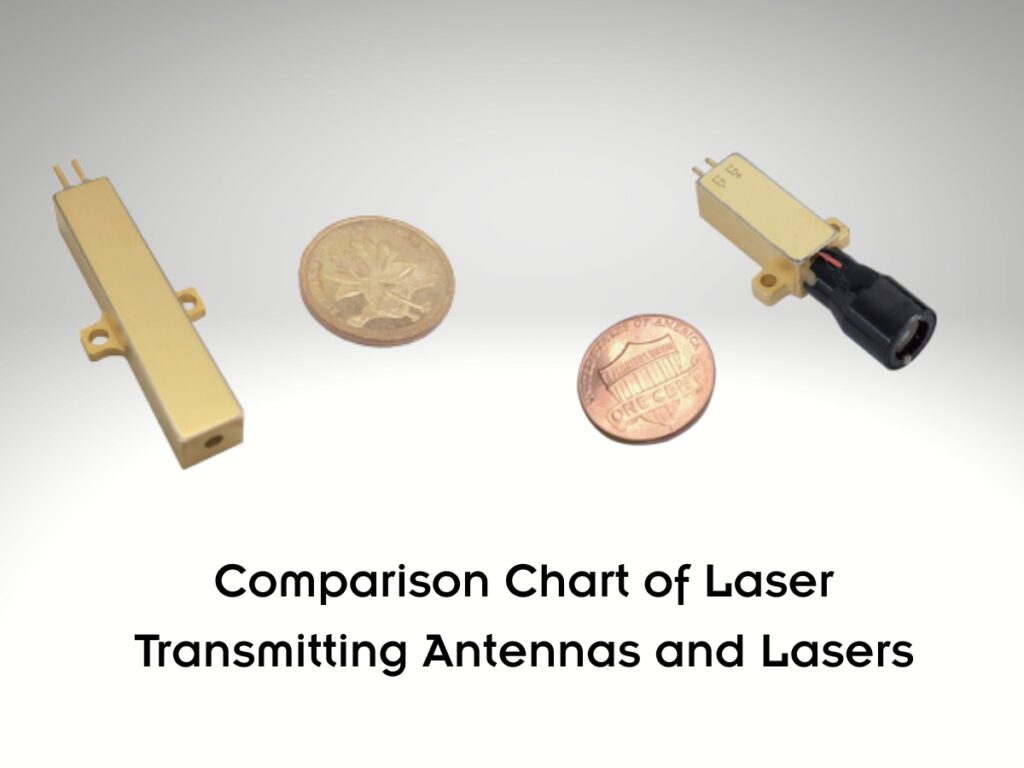
In the realm of precision photonics, understanding the distinction between a Laser Transmitting Antenna and a Laser module (also called laser transmitter) is critical for optimal system performance. Especially for 1535nm erbium glass laser systems—renowned for eye safety and harsh-environment reliability—choosing the right component can make or break applications like tactical communications, long-range sensing, and industrial measurement.
Core Definitions: What Each Component Does
A Laser module (laser transmitter) is the “heart” of the system, generating coherent laser light through stimulated emission. For 1535nm systems, erbium-ytterbium (Er,Yb) co-doped glass serves as the gain medium, producing pulses with controlled energy and repetition rate. These modules integrate key components like laser diodes, passive Q-switches, and thermal management systems to ensure stability.
A Laser Transmitting Antenna (laser emission antenna) is the “delivery system,” optimizing how laser energy propagates. It shapes the beam, enhances directionality, and matches impedance with the transmission environment—critical for minimizing signal loss and maximizing range. Unlike generic antennas, laser-specific designs prioritize beam quality and frequency matching to the laser module’s output.
Key Differences: Performance & Application
| Specification | Laser Module (Erbium Glass Laser Transmitter) | Laser Transmitting Antenna |
|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Generates eye-safe 1535nm laser pulses | Focuses and directs laser energy |
| Key Metrics | Pulse energy (100μJ–1000μJ), repetition rate, beam quality (M²) | Gain, VSWR (<2.0), polarization consistency |
| Critical Features | Thermal stability (-40°C to 65°C), shock resistance | Impedance matching (50Ω), energy concentration |
| Typical Applications | Signal source for ranging, communications | Extending range in free-space optical systems |
Our 1535nm erbium glass laser modules stand out with pulse energy options from 100μJ to 1000μJ, paired with F01/F02 series Laser Transmitting Antennas optimized for the same wavelength. This synergy ensures minimal power reflection and maximum transmission efficiency—essential for long-range sensing (>20km) and tactical communications.
Real-World Relevance: Why Matching Matters
Using a mismatched Laser Transmitting Antenna with your Laser module leads to critical issues: signal attenuation over 20dB, reduced communication range, and potential module damage from reflected power. For example, our F01 series antenna (100-300μJ) paired with the corresponding 1535nm laser module maintains VSWR ≤2.0, ensuring efficient power transfer and stable performance in extreme temperatures.
These components are engineered for defense, industrial, and IoT applications, leveraging 1535nm’s eye-safe advantage and low atmospheric attenuation (0.1dB/km). The laser module’s compact design (integrating Er,Yb:glass and Co:Spinel key components) and the antenna’s directional gain work together to deliver reliable performance in harsh conditions.
FAQ
- What’s the difference between a Laser Transmitting Antenna and a standard antenna?Laser Transmitting Antennas are frequency-matched to laser modules (e.g., 1535nm) and optimize beam directionality, while standard antennas focus on radio frequency transmission.
- Can I use any Laser Transmitting Antenna with my 1535nm Laser module?No—matching pulse energy (e.g., F02 series for 100-200μJ modules) and impedance (50Ω) is crucial to avoid signal loss and component damage.
- Why choose 1535nm erbium glass laser components?The 1535nm wavelength is eye-safe, penetrates smoke/mist, and minimizes atmospheric attenuation—ideal for tactical and industrial applications.