Time-of-Flight (TOF) laser rangefinders deliver precise distance measurements, but unlocking their full potential requires mastering the host computer software. This guide walks you through installation, configuration, and data interpretation for optimal performance.
1. Software Installation and Setup
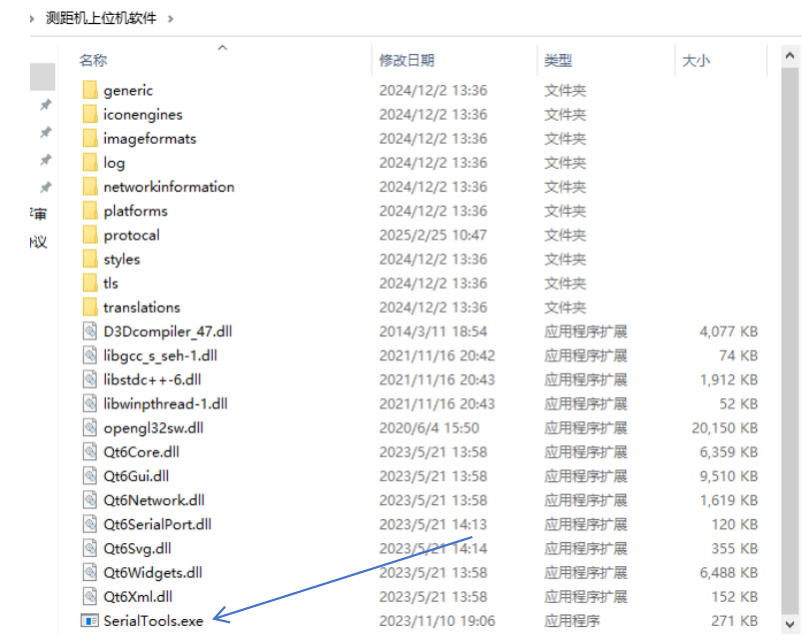
Decompress and Launch
After downloading the software package, decompress the files and launch the debugging application. Ensure your system meets the software requirements (typically Windows 7 or later with .NET Framework support).
Key Tip: Disable antivirus software temporarily during installation if you encounter false positives, as some diagnostic tools may trigger security alerts.
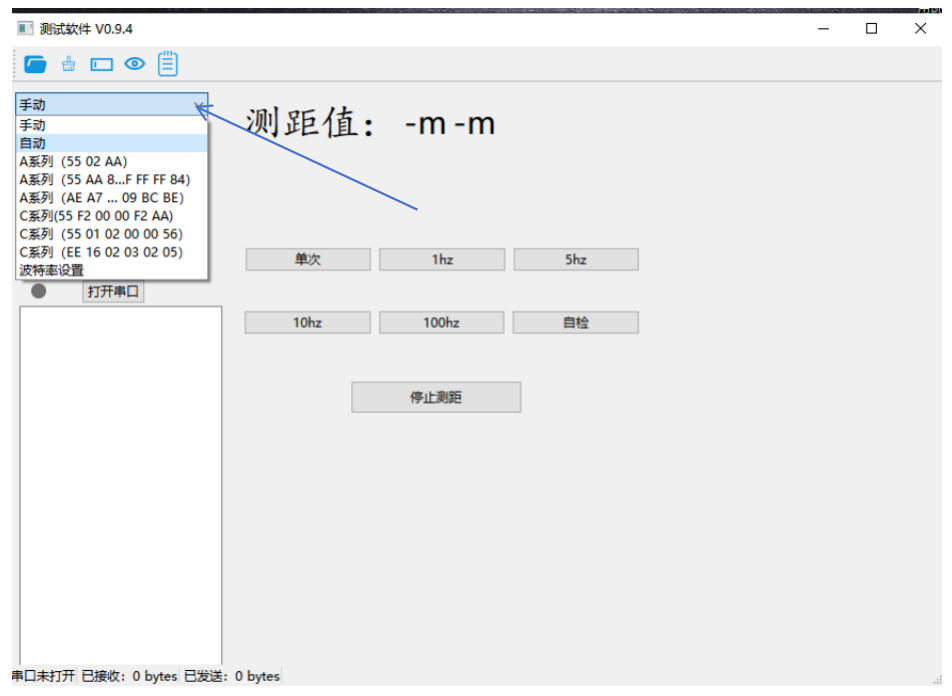
2. Protocol Selection: Matching Your Device
Understand Your Rangefinder’s Protocol
Refer to your product manual to identify the correct communication protocol. For example, if your device uses the “55 02 AA” command for single-range measurement, select the ”A-Series (55 02 AA)” protocol in the software.
Why This Matters: Using the wrong protocol will prevent communication with your device, resulting in no data response.
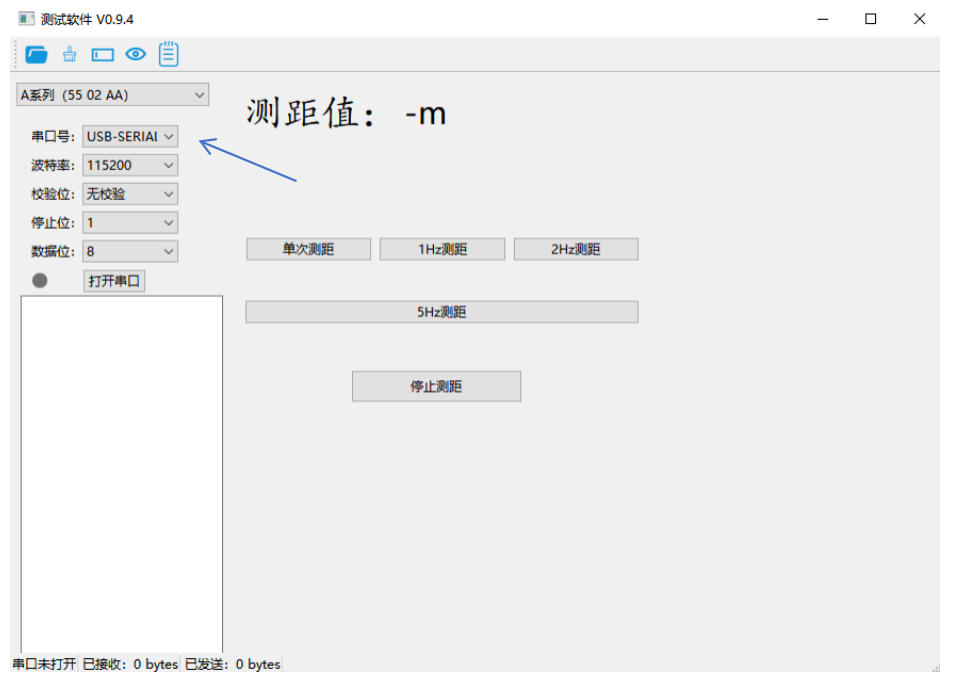
3. Serial Port Configuration
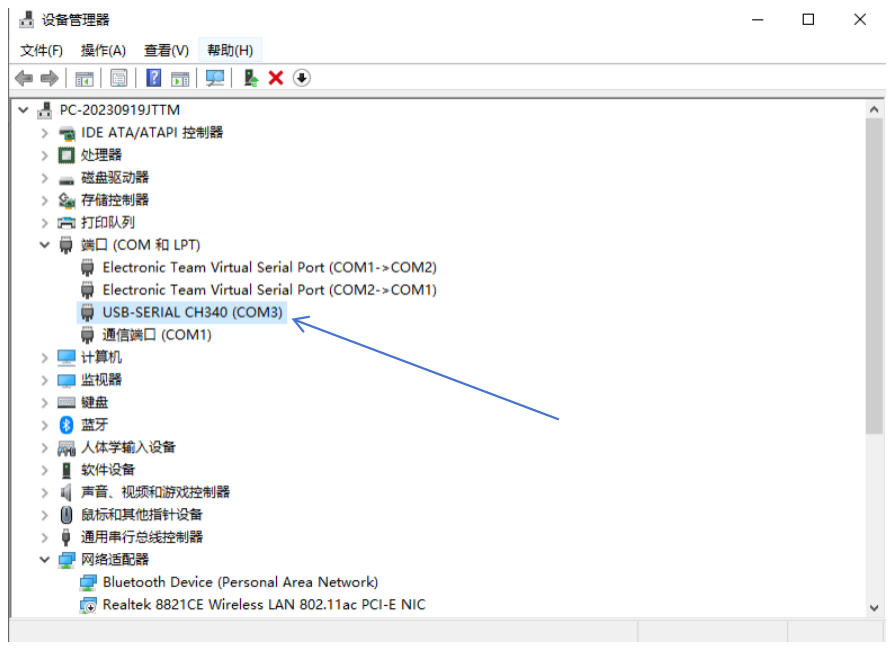
Identify Your COM Port
Check your computer’s Device Manager to identify the correct COM port. When using a CH340 TTL-to-USB converter (a common interface module), the port typically appears as COM3.
Troubleshooting Tip: If the port doesn’t appear, reinstall the CH340 drivers or try another USB port.
4. Establishing Communication and Measuring
Initialize Connection
Click “Open Serial Port” to establish communication. A successful connection is typically indicated by a status message or LED indicator change on your device.
Measurement Modes
Single Range: Takes one measurement per command
Continuous Range: Continuously measures until stopped
Stop Ranging: Halts continuous measurement
Critical Note: In continuous ranging mode, the device can only respond to “Stop Ranging” commands. Plan your measurement sequence accordingly.
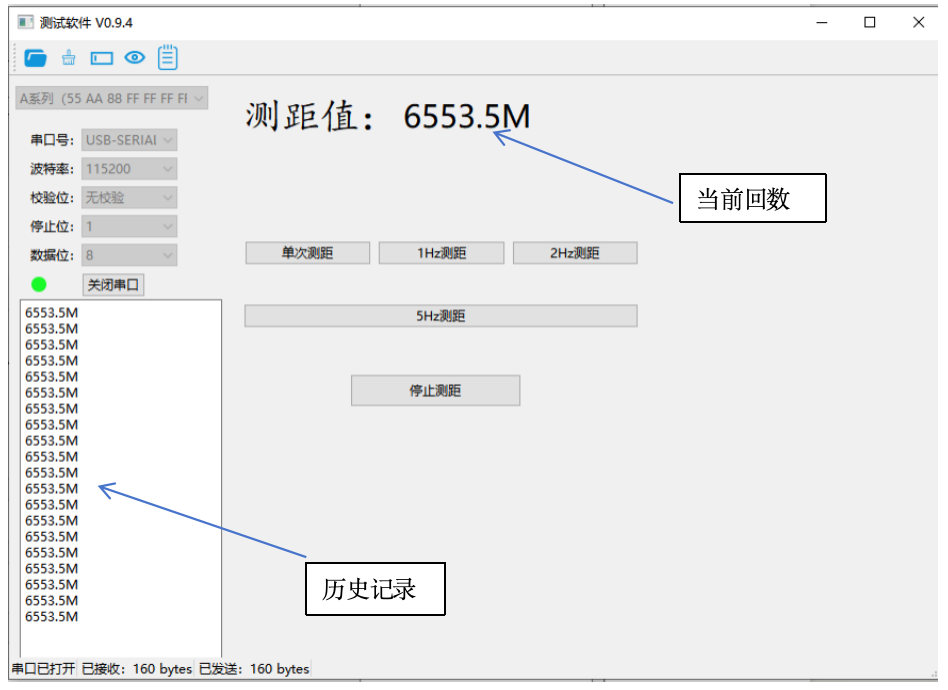
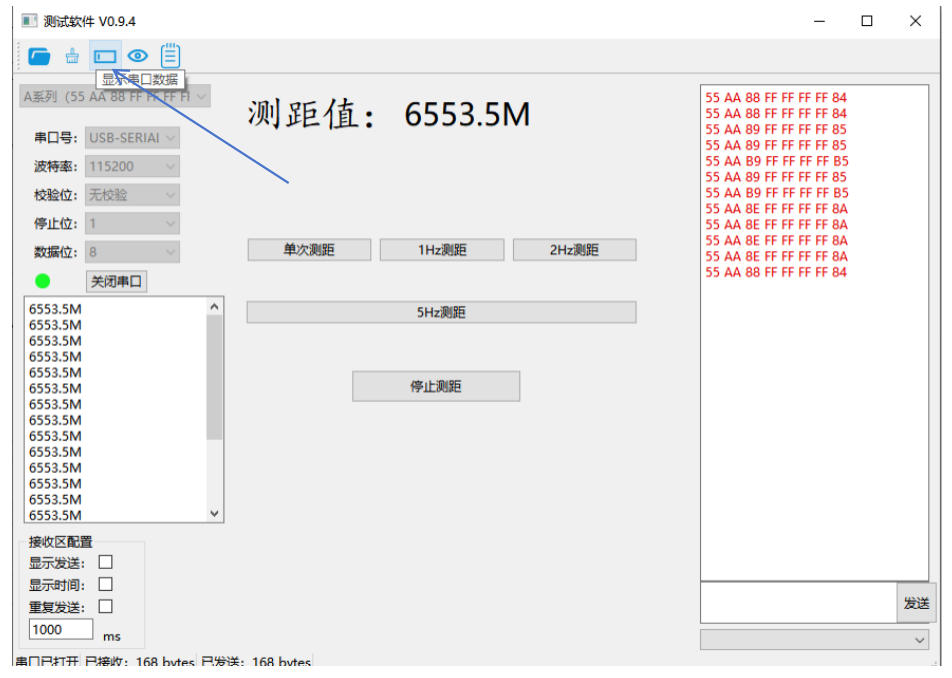
5. Data Interpretation and Analysis
Valid vs. Invalid Data
The software parses returned data into readable distance values. Watch for these invalid data indicators:
65535m: Typically indicates no target detected or signal loss
6553.5m: Often represents signal processing errors
0m: Usually indicates measurement out of range or hardware issues
Raw Data Access
For advanced analysis, click the designated area to view raw, unprocessed data from the module. This is essential for debugging and protocol development.
6. Advanced Features and Optimization
Data Logging
Most software allows saving measurement sequences for later analysis. Use this for long-term monitoring or quality control applications.
Parameter Customization
Advanced users can modify measurement parameters like pulse frequency, averaging settings, and environmental corrections for specialized applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why does the software show “No Connection” when I open the serial port?
A: Check your COM port selection, ensure drivers are installed, and verify that no other software is using the same port. Restart the software and try different USB ports if necessary.
Q2: What does 65535m distance reading mean?
A: This typically indicates no valid target detected. Check that the target is within range, has sufficient reflectivity, and that there are no obstructions in the beam path.
Q3: Can I use this software with different TOF rangefinder models?
A: The software supports multiple protocols, but you must select the correct one for your specific device. Consult your device’s documentation for protocol compatibility.
Q4: How do I improve measurement accuracy in bright sunlight?
A: Use a laser target plate or choose targets with higher reflectivity. Avoid measuring toward shiny or transparent surfaces that can cause signal scattering.
Q5: The continuous ranging mode isn’t stopping when I click “Stop.” What should I do?
A: Ensure you’re using the correct stop command for your protocol. If the issue persists, close the serial port and reopen it, which will reset the connection.